2.2- What is Geography
What do Geographers Study
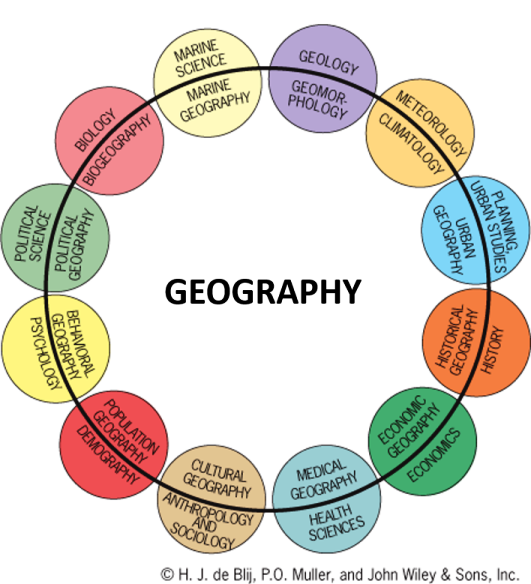 Everything! Most students think that geography is memorizing the names and locations of countries, cities, capitals, rivers, etc. But geography is so much more than that. In a nutshell, Geography answers the question “What is where and why?” Just as historians explore change over time, geographers explore change over space. There are Geographers studying history, agriculture, biology, economics etc. What makes them Geographers and not Historians or Biologists is this interest in where what they study occurs, why that phenomenon is located where it is, how this changes through time.
Everything! Most students think that geography is memorizing the names and locations of countries, cities, capitals, rivers, etc. But geography is so much more than that. In a nutshell, Geography answers the question “What is where and why?” Just as historians explore change over time, geographers explore change over space. There are Geographers studying history, agriculture, biology, economics etc. What makes them Geographers and not Historians or Biologists is this interest in where what they study occurs, why that phenomenon is located where it is, how this changes through time.
Geographers are true generalists by definition and have learned about many fields of study and how they intersect. Geography is interdisciplinary, pulling together different fields of study and looking for patterns and interrelationships.
Major Divisions in Geography
Geography is generally divided into two distinctive foci: Human Geography and Physical Geography. The reality is that these divisions are somewhat artificial and given the interdisciplinary nature of Geography, Geographers often incorporate elements of both in their studies. That said, Geographers do frequently focus on either Physical or Human Geography.
Human or Cultural Geography includes: language, religion, different economic and governmental structures, art, music, and other cultural aspects that explain how and/or why people function as they do in the areas in which they live. Globalization Links to an external site. is becoming increasingly important to the field of human geography as it is allowing these specific aspects of culture to travel across the globe easily.
Physical Geography
Physical geography consists of many diverse elements. These include: the study of the earth's interaction with the sun, the seasons, the composition of the atmosphere, atmospheric pressure and wind, storms and climatic disturbances, climate zones, microclimates, the hydrologic cycle, soils, rivers and streams, flora and fauna, weathering, erosion, natural hazards, deserts, glaciers and ice sheets, coastal terrain, ecosystems, geologic systems, and so much more.
Four broad areas interest Physical Geographers:
The atmosphere includes research areas such as the ozone layer, the greenhouse effect, wind, jet streams, and weather.
The biosphere concerns living things on the planet and why they live where they do, with topics from ecosystems and biomes to food webs and the carbon and nitrogen cycles.
The study of the lithosphere includes geological processes, such as the formation of rocks, plate tectonics, earthquakes, volcanoes, soil, glaciers, and erosion.
Geographers Tools

Regardless of what speciality a Geographer may adopt, all Geographers rely on tools to help them explain and explore their area of interest. These tools include: maps, globes, the Geographic Grid, remote sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Geographers use these tools to analyze and explain the world spatially.
In this Class
We will focus on:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Geographers Tools: the Geographic Grid, Maps, Remote Sensing
- The movement of the Earth through space and the Seasons
- Weather
- Atmospheric Disturbances
- Climate
- Vegetation
- Minerals and Rocks
- The Structure of the Earth
- Landform Processes and Landforms
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
