Greenhouse Effect
- Due Nov 7, 2023 at 12:30pm
- Points 11
- Questions 11
- Available Aug 5, 2023 at 12am - Dec 3, 2023 at 11:59pm
- Time Limit None
- Allowed Attempts 3
Instructions
Remembering that weather is the day to day fluctuations in temperature, wind, humidity, solar radiation (and more) while climate is the long term pattern of these factors, we can delve into different factors that affect climate. Here are some important factors affecting climate:
- the earth's orbit around the sun + the tilt of the earth---> leads to seasonality
- The curvature of the earth and the angle of the sunlight hitting the earth--> lead to differences based on latitude ( the equator vs. the poles vs. temperate latitudes)
- ocean currents ( we have a cold ocean current off of our coast and it keeps our summers foggy)
- El niño events lead to large amounts of rainfall in some locations and drought in others.
But we are going to focus on one particular factor that affects climate: the greenhouse effect. In particular you should be able to answer these questions from the Study Guide
- What is the Greenhouse Effect?
-
- What are the different forms of energy that are involved in the greenhouse effect?
- How do each of these contribute to the effect?
- What is the role of atmospheric gases in the greenhouse effect?
- What are the 3 most important greenhouse gases?
- Without these gases, what would happen to the earth's atmosphere?
- With increase of these gases, what is happening to the earth's atmosphere?
- How do we measure greenhouse gases in the atmosphere?
Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouses have walls and roofs made of glass. Sunlight (visible and UV wavelengths) passes through the glass, but the heat and warmth (infrared wavelength) that the sunlight creates can not escape back through the glass. This traps the heat in the building making it warmer than the outside temperatures. This same phenomenon is what happens on a sunny day to your car.
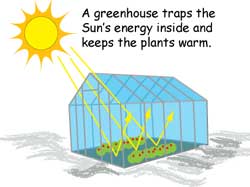
The gases in the earth's atmosphere function in exactly the same way, trapping the heat (infrared wavelengths). In general, this is a good thing, since otherwise the history of earth would have been too cold for life as we know it! There are three main greenhouse gases:
-
-
-
-
- Water vapor (H2O)
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
- Methane (CH4)
-
-
-
But what happens if we increase the amount of these gases in the atmosphere? Could we make the planet TOO
Below are 3 separate videos that each explain the greenhouse effect slightly differently and in increasing levels of complexity. Watch all three in order, so that you understand what is happening when the suns energy enters the atmosphere, hits the earth and is reradiated back towards the atmosphere, and how certain gases in the atmosphere are good at trapping some of that heat energy.
Video 2: more complex
And the last and more complete explanation